We introduce methods for enhancing relationships and creating generative and autonomous groups, centered on various forms of dialogue.
In the midst of busy daily operations, members often become trapped in narrow or short-term perspectives, losing sight of the ability to grasp the whole picture (overview), confirm the reason for their presence and actions (sense of purpose), and align on shared goals (vision, mission & values). To break free from this and become an autonomous, collaborative organization, it is first necessary to create a new space where people can genuinely listen to one another’s inner voices—a simple yet unprecedented endeavor.
INTEG’s approach is based on the concept that “when conversations change, the future changes,” and we support organizations in fostering autonomy, energy, and creativity.
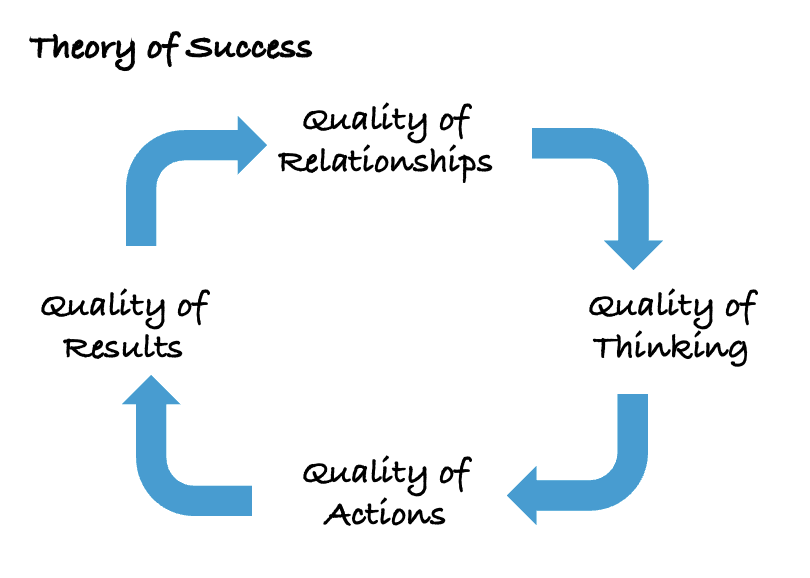
The above is the “Theory of Success” by Daniel Kim, co-founder of the MIT Center for Organizational Learning. The four qualities can lead to either positive or negative cycles. In dialogue-based organizational development, we believe it is important to focus on “the quality of relationships” to support positive cycles. To this end, we prioritize dialogues that enhance “the quality of conversation.”
▪️ Appreciative Inquiry
A process of discovering and recognizing (appreciating) the value and strengths of individuals and the true value of the organization as a whole through questioning and inquiry, and creating the most effective and capable system that maximizes the potential of those values. It was proposed in 1978 by Professor David Cooperman of Case Western Reserve University and Diana Whitney of the Taos Institute, and has been used by Hewlett-Packard, Johnson & Johnson, Nokia, AMEX, Motorola, BMW, Philips, Pfizer, the US Navy, various town development projects, and the United Nations Global Compact.
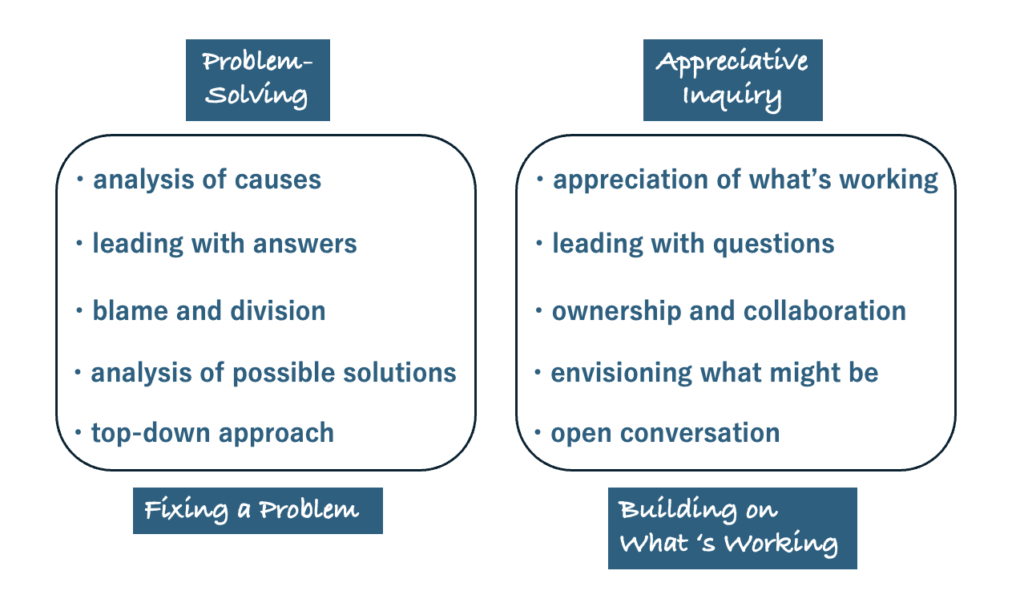
As stated in positive psychology (Professor Martin Seligman), positive thinking increases motivation and energy, leading to better results. The “positive approach” focuses on positive aspects such as strengths and possibilities, rather than the traditional “problem-solving approach” that focuses on organizational flaws and weaknesses and seeks to resolve them. By removing negative, passive, and fixed frameworks, this approach enables the creation of strategies and plans that go beyond mere improvement and hold great potential for the entire organization.
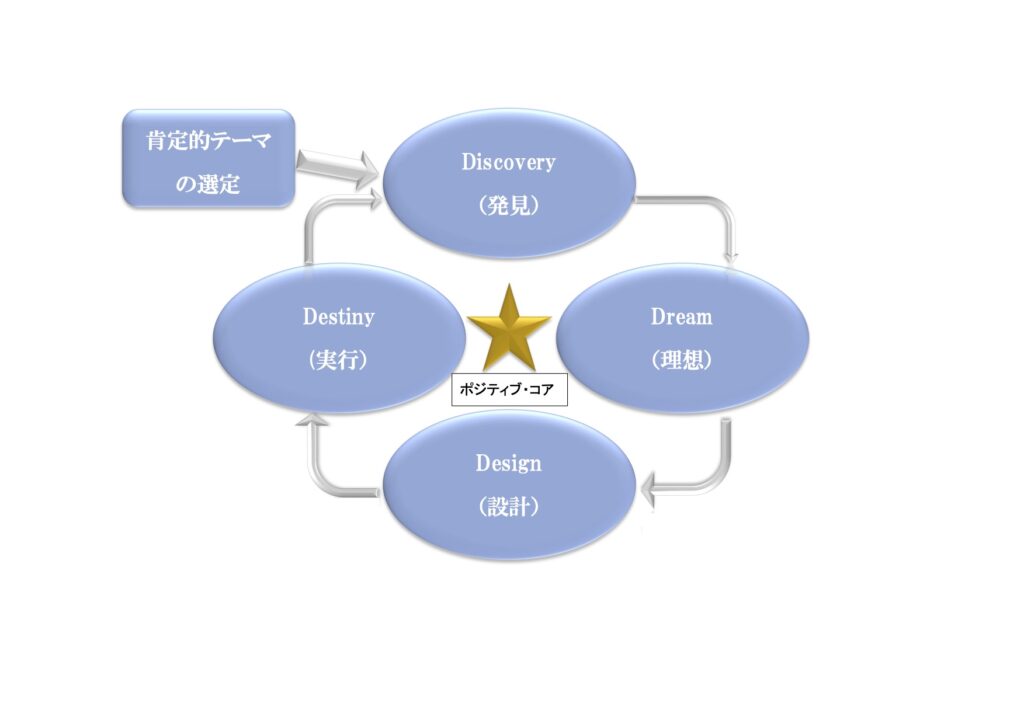
Appreciative Inquiry can be conducted in various ways, but the basic form follows a “4D cycle” process: Discovery (identifying strengths) → Dream (envisioning ideals and possibilities) → Design (determining feasible methods) → Destiny (sustaining change).
Appreciative Inquiry is an approach that can be applied not only to organizational development but also to a wide range of purposes, including individual leadership, vision making and team building.
▪️ Whole System Approach
The whole system approach does not aim for top-down decision-making or majority rule. Rather, it is a method for people with different positions and opinions and conflicting interests (multiple stakeholders) to work together to reach a consensus that is acceptable to all and realize a desirable future.
When a diverse group of stakeholders gather and engage in conversation that mobilizes the collective brain, new knowledge is created. Additionally, as autonomy and commitment naturally emerge, a process of “self-organization” occurs, where the group builds itself up as a “living organism” rather than a machine.
The background behind the need for this approach includes: (1) the expansion of interdependent relationships, (2) the loss of meaning in using past experiences to envision the future (refer to Adam Kahane’s “Three Complexities”), (3) The limitations of traditional transformation methods (4) Changes in decision-making processes (5) The growing interest in innovation.
—From “The Whole System Approach: A Method for Thoroughly Discussing Issues with Over 1,000 People” (Katori Kazuaki, Okawa Tsune)
The methods used in the Whole System Approach include the following, which are applied depending on the purpose and phase of the process:
●World Café
●AI (Appreciative Inquiry)
●Open Space
●ProAction Café
●Future Search
●Storytelling
●others
▪️ Art of Hosting (AoH)
The Art of Hosting (AoH) is a training method that involves learning through the practice of participatory leadership. In an increasingly complex environment, participants aim to create self-directed groups where they can discuss “important matters” together. Under the guidance of a coach, participants host (facilitate) their own dialogue sessions. Additionally, harvesting (recording and visualizing) the discussions to help connect them to action is an important part of AoH.
AoH employs various dialogue frameworks such as World Café, Open Space, AI (Appreciative Inquiry), storytelling, and ProAction Café.
It has been utilized in a wide range of organizations and communities worldwide, including the European Commission, the Scottish Parliament, and healthcare reform initiatives in Columbus, Ohio.

